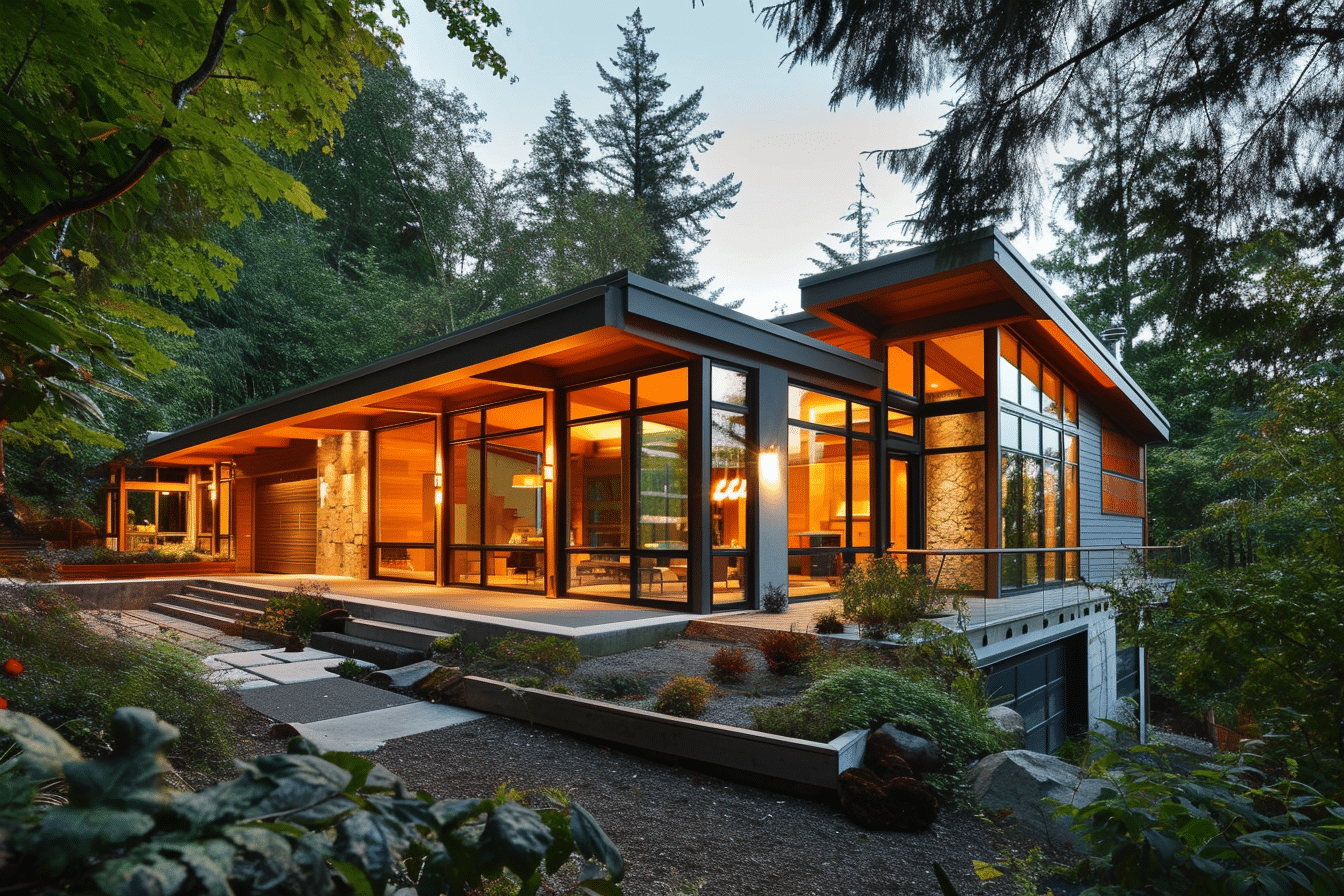
Net-Zero Homes: A Casual Guide to Sustainable Living
Net-zero homes have been gaining traction in recent years as a sustainable solution for reducing energy consumption and mitigating environmental impacts. These innovative homes are specifically designed to generate as much energy as they consume, resulting in a carbon-neutral living space. Built with energy efficiency and renewable energy in mind, net-zero homes are transforming the relationship between residential spaces and the environment.
At the core of a net-zero home lies a set of design principles and construction techniques created to optimize energy performance. These homes make use of advanced technologies to improve insulation, air sealing, and energy-efficient appliances, as well as integrating renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines. In addition to the many environmental benefits, net-zero homes also offer homeowners a healthier indoor environment and potential financial savings in the long run.
Key Takeaways from Net-Zero Homes
- Net-zero homes aim to generate equal amounts of energy as they consume, promoting sustainable living.
- Advanced construction techniques and energy efficiency technologies play significant roles in achieving a net-zero home.
- Healthier indoor environments and cost savings are additional benefits to homeowners.
Fundamentals of Net-Zero Homes
Defining Net-Zero Homes
Net-zero homes are residential buildings designed to achieve a balance between energy consumption and energy production. They combine energy efficiency and renewable energy solutions to create a comfortable, sustainable living environment. Zero energy homes and zero energy ready homes are often used interchangeably with net-zero homes, although there can be slight differences.
- Net-zero homes produce as much energy as they consume over a year.
- Zero energy homes might produce more energy than they consume, typically characterized by a negative energy bill.
- Zero energy ready homes are prepped for renewable energy systems, but might not yet produce energy on site.
Benefits of Living in a Net-Zero Home
There are several advantages associated with living in a net-zero home. Among these are:
Cost Savings
Energy-efficient homes reduce utility bills, leading to short-term and long-term financial benefits. Over time, these savings can even offset the initial investment in energy-efficient measures and renewable energy systems.
Environmental Impact
By reducing energy consumption and generating renewable energy, net-zero homes contribute to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. This helps in mitigating climate change and preserving ecosystems for future generations.
| Traditional Homes | Net-Zero Homes | |
|---|---|---|
| Energy consumption | High | Low |
| Carbon footprint | High | Low |
| Sustainability | Low | High |
Comfort and Air Quality
Energy-efficient designs and materials result in net-zero homes providing a more consistent indoor temperature. They also improve air quality by using excellent ventilation systems and eco-friendly, non-toxic materials.
Resiliency
Net-zero homes are generally more resilient during power outages and extreme weather events. As they rely on on-site energy production, they can often maintain power when the grid fails. Furthermore, their energy-efficient designs reduce the need for heating and cooling, adding to their ability to withstand harsh conditions.
In summary, net-zero homes offer a compelling combination of financial, environmental, and comfort benefits. They pave the way for a greener, more sustainable future while providing a comfortable living space for their inhabitants.
Design Principles and Construction
Building Envelope and Insulation
A net-zero home starts with the building envelope – the shell that separates the interior from the elements. This includes the walls, roof, and foundation. To achieve a high-performance home, it’s crucial to have a tight building envelope that minimizes air leakage and provides exceptional insulation.
In a typical net-zero home, insulation materials like expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), and polyiso are used to create a continuous insulation layer. This helps to reduce thermal bridging and maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Additionally, using materials like double or triple pane windows can further enhance a home’s insulation.
Orientation and Passive Design
An essential aspect of net-zero homes is their site orientation and passive design. By carefully analyzing the sun’s path and prevailing winds, architects and design-build professionals can optimize a home’s energy efficiency. Here are some essential orientation and passive design strategies to consider:
- South-facing windows to maximize solar heat gain in the winter
- Properly-sized roof overhangs to provide shade in the summer
- Strategic placement of vegetation to block or channel winds
Passive house certification is a rigorous standard for energy efficiency, and many net-zero homes aim to achieve it. By incorporating passive design principles, homeowners can substantially reduce their energy consumption and minimize their reliance on mechanical systems.
High-Performance Windows and Doors
High-performance windows and doors are crucial for any net-zero home. These fixtures not only play a role in the building envelope, but also contribute to passive solar design. When selecting windows and doors, consider the following features:
Windows:
- Double or triple glazing
- Low-E coatings to reduce heat loss
- Gas fills (such as Argon or Krypton) for improved thermal performance
Doors:
- Insulated, energy-efficient materials
- Proper weatherstripping and seals to minimize air leakage
- Energy-efficient glazing where applicable (e.g., patio doors)
By incorporating these design principles and construction techniques, a net-zero home can significantly reduce its energy consumption, provide a comfortable living environment, and take a substantial step toward sustainability.
Energy Efficiency Technologies

Smart Thermostats and HVAC Systems
To make net-zero homes a reality, the energy efficiency of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems plays a crucial role. A great way to achieve this is by incorporating smart thermostats into your home. These intelligent devices learn your habits and preferences, adjusting the temperature to maximize energy efficiency. As a result, homeowners can save both energy and money on their utility bills.
Another way to boost energy efficiency is by upgrading the HVAC system itself. High-performance homes often feature low-energy HVAC systems, such as variable-speed air conditioners and modulating furnaces. These systems are designed to run at lower energy consumption levels, maintaining a comfortable home environment and reducing the carbon footprint simultaneously.
Heat Pumps and Mechanical Systems
Heat pumps serve as impressive energy-efficient alternatives to traditional heating and cooling systems, acting as a key component in many net-zero homes. They work by transferring heat from one area to another, allowing for efficient heating in colder months and cooling during the warmer seasons.
Different types of heat pumps include:
- Air-source heat pumps
- Ground-source (geothermal) heat pumps
- Water-source heat pumps
- Absorption heat pumps
Each type boasts its distinct advantages and installation requirements, but all offer energy-saving benefits that can contribute to a comfortable, environmentally-friendly living space.
Energy-Efficient Lighting and Appliances
To minimize energy consumption, net-zero homes tend to use energy-efficient lighting and appliances. One popular option is LED lighting, which uses less power and has a longer lifespan than traditional incandescent or compact fluorescent lights.
Selecting energy-efficient appliances is also essential. Look for devices with a high Energy Star rating or similar certification – these appliances consume less energy in their daily operations without sacrificing performance. Examples include:
| Appliance | Energy Efficiency Impact |
|---|---|
| Refrigerators | 10-30% less energy |
| Dishwashers | 12-30% less energy |
| Clothes washers | 25% less energy and 45% less water |
By utilizing these energy efficiency technologies, net-zero homes can achieve their goal of reducing, or even eliminating, their dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Renewable Energy Integration

Solar Panel Systems
Integrating solar panel systems into net-zero homes is a key aspect of achieving high energy performance. These renewable energy systems efficiently convert sunlight into electricity, significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering energy bills. Some important components to consider when designing and installing solar panels include:
- Type of solar panels: Monocrystalline, polycrystalline, and thin-film panels offer varying levels of efficiency, aesthetics, and prices.
- Roof size and angle: Assessing the available roof space and angle helps in determining the optimal size and layout of the solar system.
- Storage capacity: Solar energy can be stored in batteries for later use, ensuring a continuous power supply even on less sunny days.
A well-designed solar panel system will maximize the energy output and contribute to a significant portion of a net-zero home’s energy needs.
Other Renewable Energy Sources
While solar panels are often the first renewable energy source considered in net-zero homes, there are other alternatives available to further improve energy performance. Some of these options include:
- Wind turbines: Small-scale wind turbines can be installed on properties, particularly in rural or windy areas, to supplement solar power generation.
- Geothermal energy: Geothermal systems use the Earth’s natural heat to provide heating and cooling for a home. These systems require initial investment, but can lead to long-term energy savings.
- Micro-hydro power: For homeowners with access to a continuous water source, micro-hydro power systems can be an effective way to generate electricity.
Integrating various renewable energy sources into a net-zero home ensures a sustainable and self-sufficient energy supply, reducing dependency on traditional energy sources and lowering environmental impact. Combining solar panels with other renewable energy systems can further enhance a home’s overall energy performance and comfort.
Regulations and Incentives

Energy Efficiency Standards and Certifications
In order to promote the construction of net-zero homes, various energy efficiency standards and certifications have been established. Notably, the DOE Zero Energy Ready Home Program sets a high level of performance for residential buildings. Homes built under this program must meet strict guidelines, ensuring they are more energy-efficient than typical homes.
However, not all energy-efficient homes achieve net-zero status. Therefore, it’s essential to be aware of the different standards and certifications that can contribute to a home’s overall energy efficiency and potential for reaching net-zero.
Government Incentives and Tax Credits
Government incentives play a significant role in promoting net-zero home development. Primarily, financial incentives like tax credits assist homeowners in offsetting the costs of installing energy-efficient systems and appliances.
In the United States, the DSIRE (Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency) is an invaluable resource for finding information on local and federal incentives. State and local governments offer various incentives tailored to their region’s energy goals.
It is important to research and take advantage of available tax incentives and government programs to make building or retrofitting a net-zero home more affordable and feasible. By combining energy efficiency standards and certifications with financial incentives, achieving a net-zero home becomes increasingly achievable for homeowners.
Costs and Financial Considerations

Initial Costs vs Long-Term Savings
When considering a net-zero home, it’s essential to weigh the initial costs against the potential long-term savings. While the upfront investment might be higher for a net-zero home compared to a traditional home, the energy savings over time can offset these costs.
For instance, a net-zero home typically involves added expenses for:
- High-efficiency appliances and lighting
- Enhanced insulation
- Solar panels or other renewable energy systems
However, these improvements can lead to significant energy savings in the long run, lowering monthly utility bills and potentially saving thousands of dollars over the lifespan of the home.
Affordability and the Market
The market for net-zero homes is continuously evolving, which is good news for those concerned about affordability. With increased demand and advancements in technology, the costs of constructing and purchasing a net-zero home are becoming more competitive with traditional homes.
Some factors affecting the affordability of net-zero homes include:
- Regional energy costs
- Availability of energy-efficient materials and systems
- Government incentives or subsidies
In many cases, energy-efficient and zero-energy-ready homes are becoming more accessible to a broader range of buyers, contributing to the growth of the sustainable housing market.
In conclusion, when considering the costs and financial aspects of net-zero homes, it’s essential to weigh the initial investment against the long-term savings in energy costs. With an ever-growing market and increased affordability, net-zero homes are becoming a more viable option for many homebuyers.
Health and Indoor Environmental Quality

Indoor Air Quality and Ventilation
A key aspect of net-zero homes is their focus on maintaining excellent indoor air quality. This is achieved primarily through a combination of well-insulated structures, energy-efficient ventilation systems, and careful material selection. In these homes, occupants can expect to breathe in fresh, clean air at all times.
One may wonder, how do net-zero homes manage to maintain such high indoor air quality? It’s thanks to the use of heat recovery ventilation (HRV) systems. These modern marvels not only minimize heat loss but also continuously supply the home with fresh, filtered outdoor air. They provide proper ventilation while reducing the concentration of indoor pollutants such as carbon dioxide and allergens.
Health Benefits of Net-Zero Homes
Living in a net-zero home is not only an eco-friendly choice but can also provide numerous health benefits. Here are a few reasons why they are excellent for your well-being:
- Reduced allergens: By ensuring a constant supply of fresh outdoor air, net-zero homes can significantly reduce the presence of allergens in the indoor environment, leading to improved respiratory health.
- Balanced temperatures: Thanks to their well-insulated walls, floors, and ceilings, these homes maintain comfortable and consistent indoor temperatures all year round, contributing to better sleep quality and overall comfort.
- Lower humidity: Net-zero homes usually utilize moisture management techniques to control humidity levels, preventing problems like mold growth and improving indoor air quality.
- Chemical-free building materials: Health-conscious builders prioritize the use of low-VOC materials in net-zero homes, reducing the presence of toxic chemicals in the indoor environment.
In summary, living in a net-zero home can contribute positively to both physical and mental health, by providing a comfortable, well-ventilated, and healthy indoor environment. Investing in such a property is not only a decision for the planet but also for personal well-being.
Net-Zero Home Case Studies

Individual and Tiny Homes
One great example of net-zero homes can be found in the form of a pilot project of 35 Net-Zero Energy Ready homes built in 2020 in Quebec, Canada. These homes, designed to meet the demands of climate change and promote green living, were built with optional solar PV for Net-Zero certification in a cold climate zone.
As for tiny homes, they integrate highly efficient space-saving designs while minimizing energy consumption. They can be constructed to achieve net-zero energy use, often through the installation of solar panels and advanced insulation techniques. This makes tiny homes an excellent example of how the built environment can contribute to mitigating climate change.
Production and Community-Scale Projects
Moving on to larger scale projects, production homes have started to embrace the net-zero home concept by incorporating advanced building techniques and renewable energy technologies. For instance, home developers are utilizing energy-efficient windows, improved insulation, and solar panels to produce as much energy as the home consumes over the course of a year.
On a community level, net-zero neighborhoods or eco-villages are emerging as innovative solutions to address climate change and support sustainable living. These communities consist of multiple net-zero homes, shared green spaces, and local renewable energy resources.
A notable example of a net-zero community is showcased by the Zero Energy Project. These types of communities not only promote better energy efficiency, but also encourage the incorporation of renewable resources and sustainable practices throughout the community, ultimately fostering a positive impact on the environment.
Net-Zero Homes in Oklahoma
Net-zero homes are a revolutionary step towards sustainable living, and Oklahoma is at the forefront of this movement. In the Sooner State, the construction of the first zero-energy home priced under $200,000 marks a significant milestone. This was in 2006 in Valencia.
This innovative dwelling is designed to produce as much energy as it consumes over the course of a year, balancing energy efficiency with affordability. The integration of advanced building techniques and renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, allows homeowners to enjoy a greener lifestyle without sacrificing comfort or breaking the bank.
This achievement not only showcases the potential for energy-neutral housing in Oklahoma but also sets a precedent for future home construction nationwide.
Challenges and Future Outlook

Technological and Design Challenges
In the pursuit of net-zero homes, there are significant technological and design challenges to overcome. One primary hurdle is the integration of renewable energy systems with the electrical grid. As renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines continue to gain popularity, it’s crucial to ensure they operate seamlessly with the existing infrastructure.
Additionally, retrofitting older homes with energy-efficient technology is often complicated and costly. Homeowners may face challenges related to code compliance, as well as budget and logistical constraints. To address this, innovative solutions are necessary to make the retrofit process more accessible and enticing to homeowners.
When designing net-zero homes from scratch, architects and engineers face unique challenges as well. Adapting their designs to the local climate is essential to achieve net-zero status. For instance, homes in colder climates may require more insulation and consider specific building materials, while those in warmer climates should optimize natural ventilation and focus on cooling strategies.
Climate Change and the Built Environment
Climate change is a pressing issue that affects various aspects of society, including the built environment. As global temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, new challenges and opportunities arise for net-zero homes.
Table 1: Climate Change Impacts on Net-Zero Home Design
| Climate Factors | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|
| Rising Temperatures | Increased demand for cooling, energy | Enhance passive cooling techniques |
| Extreme Weather | Structural durability, resiliency against events | Implement eco-friendly construction materials |
| Changing Precipitation | Optimize water-efficiency | Harvest rainwater |
An essential aspect of net-zero homes is their ability to adapt and address the consequences of climate change, like increasing occurrences of extreme weather events. This adaptation may involve strengthening the structure of the buildings and using resilient, eco-friendly materials to withstand potential natural disasters.
Simultaneously, the growing emphasis on net-zero homes is a crucial step towards mitigating the effects of climate change. By reducing the greenhouse gas emissions associated with residential properties, net-zero homes contribute to a more sustainable built environment and help combat the most significant global challenge humanity faces today.
Luxury Specialist at McGraw Realtors
With a diverse background, including a career as an Air Force fighter pilot and entrepreneurship, Bill transitioned to real estate in 1995. Co-founding Paradigm Realty with his wife, Charlene, he quickly rose to prominence in Oklahoma City’s luxury real estate scene. Now, as one of the top agents with annual sales surpassing $20 million, Bill’s dedication to exceptional service remains unparalleled. With a legacy spanning over two decades in the industry, Bill’s expertise and commitment make him a trusted name in luxury real estate.